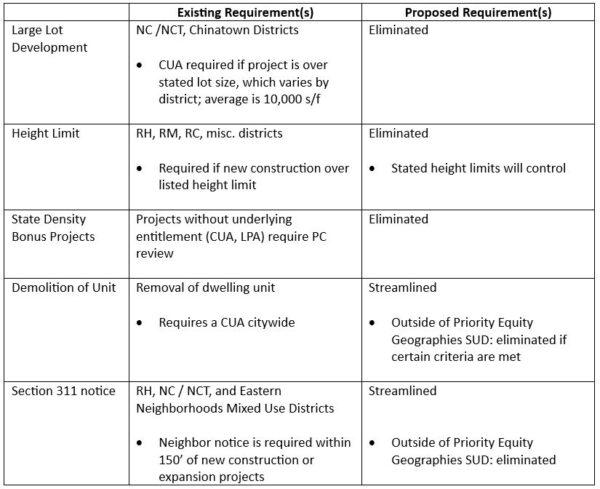
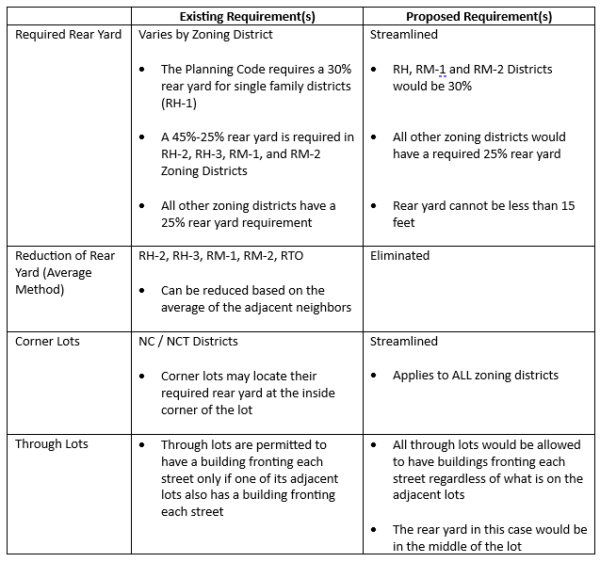
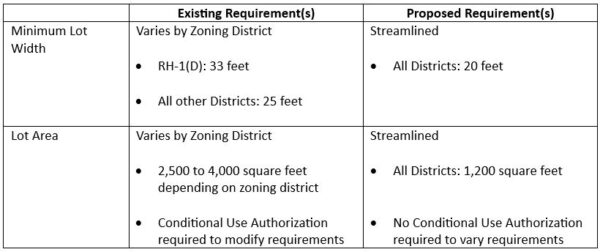
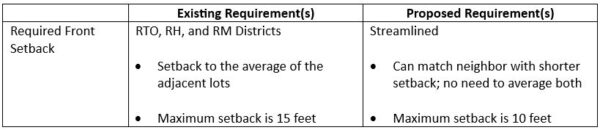
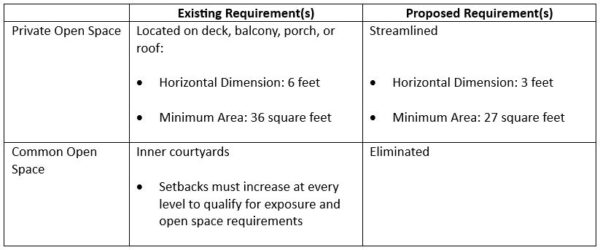
Last week the California Legislature passed SB-423, new law introduced by Senator Scott Weiner to spur statewide housing production.
SB-423 extends and expands SB-35 (Weiner, 2017), which allows streamlined, ministerial processing for housing developments in cities that haven’t met their Regional Housing Need Allocation (RHNA) goals. Qualifying SB-35 projects must also meet certain criteria, including on-site affordability and labor requirements, and comply with local objective zoning standards.
SB-35 has been celebrated by housing development advocates statewide over the past six years for unlocking the potential to develop thousands of new homes. According to an August 2023 report issued by the UC Berkeley Terner Center for Housing Innovation, SB-35 spurred applications for construction of more than 18,000 new units in California between 2018 and 2021, 62% of which were 100% affordable.
SB-423 extends the original term of SB-35 by decade, to January 1, 2036.
It also makes a number of significant tweaks to SB-35, including:
- Extending into the Coastal Zone. Previously, SB-35 did not apply to property within California’s Coastal Zone, which is a band of land that extends approximately 840 miles along California’s coast. SB-423 removes this exemption, allowing SB-35 to apply within the Coastal Zone beginning January 1, 2025, except for certain environmentally sensitive or hazardous locations, or areas not zoned for multifamily housing. Qualifying developments would still require a Coastal Zone Permit, but the public agency must approve it if they determine the development is consistent with objective zoning standards, which may be modified through state density bonus law.
- Shortening San Francisco’s Reporting Period. SB-35 applies to cities that aren’t meeting their RHNA housing production goals either for low- or above-moderate income categories, which is typically determined by the California Department of Housing and Community Development (“HCD”) every four years. However, SB-423 singles-out the City of San Francisco, requiring analysis of its RHNA goal progress (and SB-35 eligibility under each income category) every year. As of the most recent assessment, San Francsico was meeting RHNA goals for above-moderate income housing, but not low-income housing. As a result, SB-35 projects in the City must currently provide 50% of units affordable to low-income households. However, if moving forward San Francisco falls below above-moderate income housing targets in an annual review period, projects could instead qualify for SB-35 by providing 10% of on-site units as affordable. Local Inclusionary Program requirements would still apply, but affordable units under SB-35 would count toward the local requirements.
- Tying Application to Housing Element Compliance. SB-423 extends application of SB-35 to Cities that have failed to adopt a compliant housing element as determined by the California Department of Housing and Community Development (“HCD”), even if they’re currently meeting RHNA goals.
- Altering Affordability Requirements. SB-423 amends the affordability requirements for rental units in 10% jurisdictions, requiring such units to be affordable to households making 50% of the area median income, instead of the current 80%. The legislation also includes an alternate definition for “affordable rent” for developments that dedicate 100% of their units, exclusive of manager’s units, to lower income households.
- Clarifying Interaction with Local Inclusionary Programs. It specifies that if a local BMR program requires units that are restricted as affordable to AMI tiers higher than those required by SB-35, the units meeting SB-35 thresholds will satisfy the local program requirements for higher-income units.
- Amends Labor Standards. It requires projects over 85 feet in height, regardless of unit count, to utilize a skilled and trained workforce. Further, on projects with 50 or more units, contractors and subcontractors with construction craft employees must meet specified apprenticeship program and health care expenditure requirements.
- Allowing the State to Approve Development on State Property. It authorizes the California Department of General Services, at its discretion, to act in the place of the local government, at its discretion, in order to approve SB-35 projects on property owned by or leased to the state.
- Creating New Noticing Requirements. Requires local governments to hold a public meeting within 45 days of receiving a notice of intent to submit an SB-35 application for projects proposed in a census tract designated as a moderate- or low-resource area, or an area of high segregation and poverty.
- Limiting the Scope of Local Review. Expressly states that cities cannot request studies, information or other materials that are not related to determining whether the development is consistent with the objective standards, nor can they require compliance with any standards necessary to receive a post-entitlement permit before the issuance of the project’s entitlement.
SB-423 is now on Governor Newsom’s desk along with a long list of other new bills passed just before the end of the legislative session. The Governor has until October 14th to sign or veto the bill. Unless vetoed, it will take effect on January 1, 2024.
Authored by Reuben, Junius & Rose, LLP Partner Melinda Sarjapur.
The issues discussed in this update are not intended to be legal advice and no attorney-client relationship is established with the recipient. Readers should consult with legal counsel before relying on any of the information contained herein. Reuben, Junius & Rose, LLP is a full service real estate law firm. We specialize in land use, development and entitlement law. We also provide a wide range of transactional services, including leasing, acquisitions and sales, formation of limited liability companies and other entities, lending/workout assistance, subdivision and condominium work.