Palo Alto recently reached a new housing milestone. On November 13, Palo Alto’s City Council adopted a legislative package implementing rezonings originally proposed in the City’s still uncertified sixth cycle Housing Element. In addition to increasing density and height limits on specific parcels across Palo Alto, this rezoning effort will unlock multi-family residential development on certain properties zoned for industrial or commercial uses.
The City Council’s action comes after a year marked by Palo Alto’s inability to adopt a compliant Housing Element. After missing its state mandated January 2023 deadline, Palo Alto adopted a Housing Element in March. But HCD, the state agency tasked with ensuring local compliance with Housing Element Law, rejected the City’s March Housing Element forcing City planners to go back to the drawing board. A second round of Housing Element legislation passed in May but to little avail. During its review process, HCD again refused to certify Palo Alto’s Housing Element. In a letter sent to the City’s Planning Department in early August, HCD requested Palo Alto make various modifications before it would certify the City’s Housing Element, citing concerns that the City’s site inventory was insufficient. Consequently, as of the time of this publication, Palo Alto’s Housing Element is out of compliance with state law and the City may be vulnerable to further Builder’s Remedy projects. With the adoption of this legislative package, the Palo Alto City Council seeks to appease HCD in the hope that the agency will finally certify the City’s Housing Element.
In addition to modest upzoning across the city, the enacted legislation focuses on rezoning parcels identified as housing opportunity sites in the City’s Housing Element. These identified opportunity sites are primarily clustered around a handful of the City’s major transit corridors, including properties along the west side of El Camino Real between Page Mill and Matadero Avenue (the “El Camino Real Focus Area”), commercial and industrial properties near San Antonio Road and Fabian Way (the “GM/ROLM Focus Area”), and certain sites owned by Stanford University along El Camino Real and Pasteur Drive. These changes come as affected property owners and lessees along El Camino Real have expressed increasing interest in redeveloping their properties to accommodate new housing.
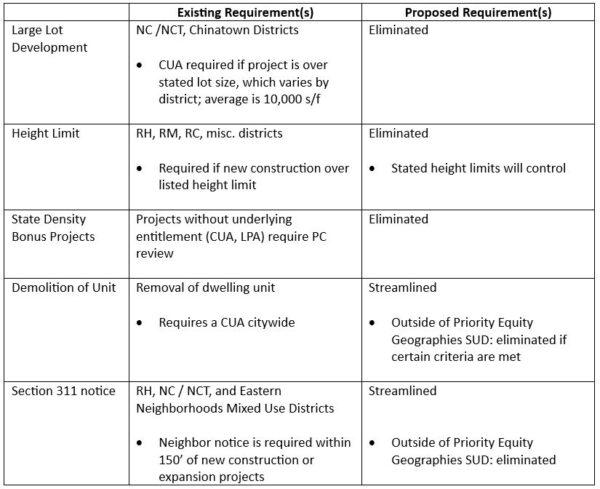
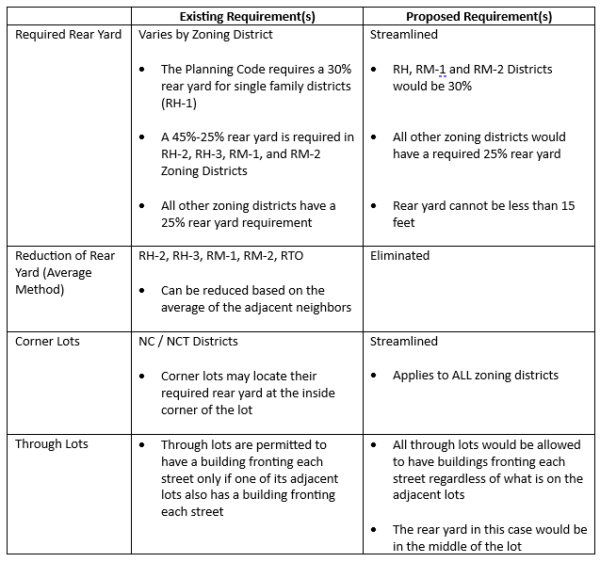
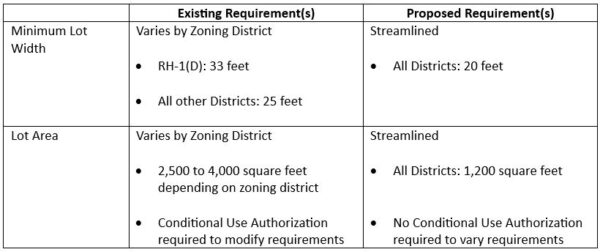
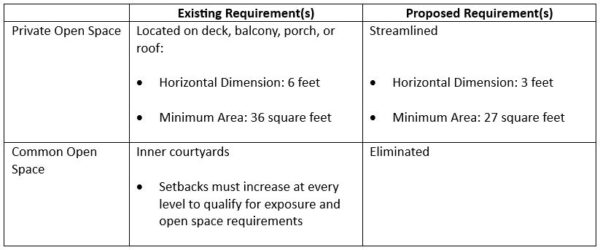
Under the adopted rezoning package, opportunity sites identified in the City’s Housing Element will be rezoned to allow multi-family housing as a permitted use and will enjoy higher density and height limits compared to base zoning. The upshot is that industrially zoned properties located in the GM/ROLM Focus Area will allow multi-family housing as a permitted use, maximum height increases, and FAR maximum increases from 0.5 to 2.5 within the focus area and 1.5 on other opportunity sites. Because these densities would represent the “base” density, developers could leverage the rezoning and use the State Density Bonus Law to construct even taller and denser buildings. Properties located in the GM/ROLM Focus Area will also enjoy modified development standards, including a relaxed landscape coverage standard, reduced parking requirements, and taller height limits further easing constraints on development and leading to more housing in Palo Alto.
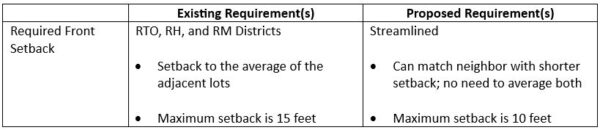
Sites identified as part of the City’s El Camino Real Focus Area will also enjoy higher densities, height limits, and lot coverage maximums. But, in response to local concerns, these projects will also face new headwinds. Residential development on these properties will be subject to architectural review to meet either objective design standards or context-based design criteria and would be required to provide 20% below-market rate housing at 80% AMI, an increase from the City’s typical requirement of 15%.
Finally, responding to demands from Stanford University, Palo Alto’s City Council also adopted higher density zoning regulations for university owned properties along El Camino Real and Sand Hill Road. Even though Palo Alto will count housing built on Stanford campus toward its RHNA, the university intends to develop these parcels with subsidized housing for graduate students, faculty, and other Stanford employees.
Beyond the focus areas identified as part of the Housing Element update, however, the rezoning also relaxes design and development standards for certain exclusively residential projects intended to accommodate lower income households across the City. Palo Alto’s recent rezoning legislation presents opportunities across Palo Alto to develop more residential housing in one of the most expensive communities in the Bay Area.
Authored by Reuben, Junius & Rose, LLP Attorney Alex Klein.
The issues discussed in this update are not intended to be legal advice and no attorney-client relationship is established with the recipient. Readers should consult with legal counsel before relying on any of the information contained herein. Reuben, Junius & Rose, LLP is a full service real estate law firm. We specialize in land use, development and entitlement law. We also provide a wide range of transactional services, including leasing, acquisitions and sales, formation of limited liability companies and other entities, lending/workout assistance, subdivision and condominium work.