As we’ve previously covered, Governor Gavin Newsom signed a substantial amount of housing bills into law this year. Two of the most notable pieces of legislation will significantly increase the state density bonus permitted under state law and will make noteworthy changes to SB 35. Below is a more in-depth look at the amendments to the State Density Bonus Law as well as an overview of the potential impacts of the amendments to SB 35 in San Francisco.
AB 1287 – State Density Bonus Law
Beginning on January 1, 2024, AB 1287 will allow an additional 20% to 50% density bonus on top of the existing maximum bonus for projects that provide additional affordable housing units. Currently, the maximum density bonus allowed under the State Density Bonus Law is 50%, which can be accomplished by providing 15% very low income, 24% low income, or 44% moderate income units. The new amendments will allow projects that qualify for a 50% bonus under the current law to provide additional very low income or moderate income affordable housing units in exchange for an additional density bonus based on the sliding scale shown below. For example, a project that provides an additional 5% very low income units, for a total of 20% very low income units, would be subject to an additional 20% bonus, for a total bonus of 70%.
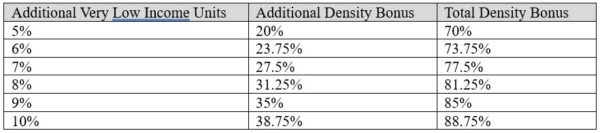
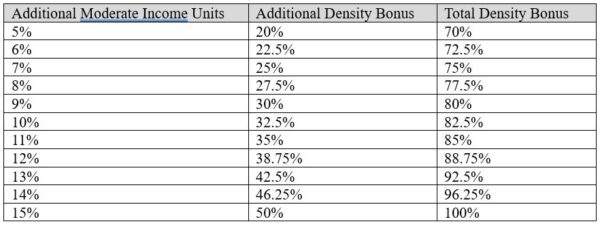
The only limit placed on projects that utilize this additional density bonus is that no more than 50% of the total units can be restricted as affordable.
The amendments also allow up to four concessions for projects that include a total of at least 16% of the units for very low-income households or at least 45% for moderate income households in for sale developments.
The bill also makes some tweaks to the requirements for 100% affordable housing projects that are proposed under the State Density Bonus law.
SB 35’s Future in San Francisco
SB 35 is a state law that offers streamlined ministerial approval for projects in cities that haven’t met their Regional Housing Need Allocation (RHNA) goals in exchange for providing affordable housing and agreeing to certain labor requirements. SB 423, which will take effect on January 1, 2024, includes a number of amendments to SB 35, as discussed in detail here.
San Francisco is currently falling short of meeting its RHNA goals for low income housing, but not above moderate income housing. So, in order to qualify for SB 35, a project in San Francisco must provide at least 50% of its units (not including units granted via a density bonus) to low-income households.
However, due to the increase in the state’s housing production goals allocated to San Francisco for the current RHNA cycle (2023-2031), it is anticipated that the City will not meet its goals for above-moderate housing in the next reporting period. If the California Department of Housing and Community Development makes that determination next summer, then a rental project will qualify for SB 35 streamlining by providing 10% of its units as affordable to very low income households or 20% of its units to low income households. An ownership project can qualify by providing 10% of its units as affordable to low income households.
SB 35 allows for ministerial approval, meaning it eliminates environmental review under CEQA and discretionary entitlements from the Planning Commission. It also imposes a maximum 6-month time frame for approval of planning entitlements. If San Francisco becomes a “10% jurisdiction,” it could unlock the ability to pursue projects that are otherwise cost-prohibitive due to long processing and approval timelines.
Together, SB 35 and the new additional density bonus could significantly spur housing development in San Francisco next year.
Authored by Reuben, Junius & Rose, LLP Attorney Sabrina Eshaghi.
The issues discussed in this update are not intended to be legal advice and no attorney-client relationship is established with the recipient. Readers should consult with legal counsel before relying on any of the information contained herein. Reuben, Junius & Rose, LLP is a full service real estate law firm. We specialize in land use, development and entitlement law. We also provide a wide range of transactional services, including leasing, acquisitions and sales, formation of limited liability companies and other entities, lending/workout assistance, subdivision and condominium work.







