There are relatively fewer new state laws affecting condominium homeowners associations (“HOAs”) in 2023 than in recent years. However, one particular bill was passed by the California State legislature that […]


There are relatively fewer new state laws affecting condominium homeowners associations (“HOAs”) in 2023 than in recent years. However, one particular bill was passed by the California State legislature that […]

Recently, Mayor London Breed and Supervisor Joel Engardio introduced an ordinance removing some of the Planning Code’s regulatory barriers to housing. A major implementing measure of San Francisco’s recent Housing […]

Last week, the Ninth Circuit struck down the City of Berkeley’s “Natural Gas Ban” in new construction regulations. The case, California Restaurant Association v. City of Berkeley, focused on whether […]

Last week, two new ordinances were introduced, both seeking to encourage residential conversion projects downtown, which have been recently touted by the media and policy advocates as one potential solution […]

As reported last week, this legislative session is packed full of pending bills with far reaching changes to land use controls and local control of such. In Part 1, we […]

As we’ve previously reported, 2022 was a blockbuster year for housing legislation and it appears this legislative session is gearing up to be just as consequential. But, with approximately a […]
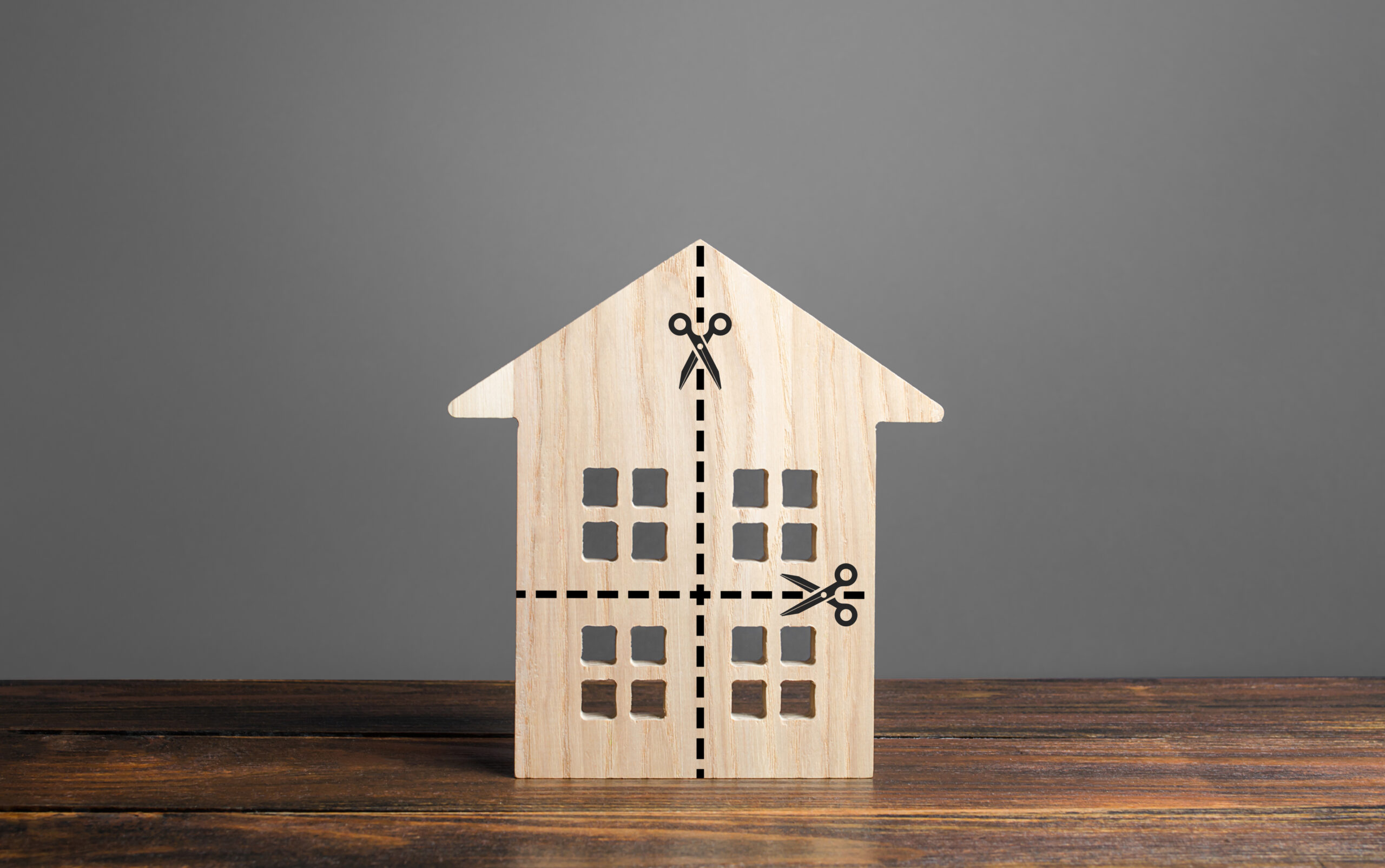

A partition action is the procedure for segregating and terminating common interests in the same parcel of real property, resulting in either: (1) a physical division of the property; (2) a […]

In the recently released Preliminary Controller Recommendations, the Inclusionary Housing Technical Advisory Committee (“TAC”) recommended reductions in San Francisco’s inclusionary housing requirements to make low- and mid-rise condo development feasible. […]
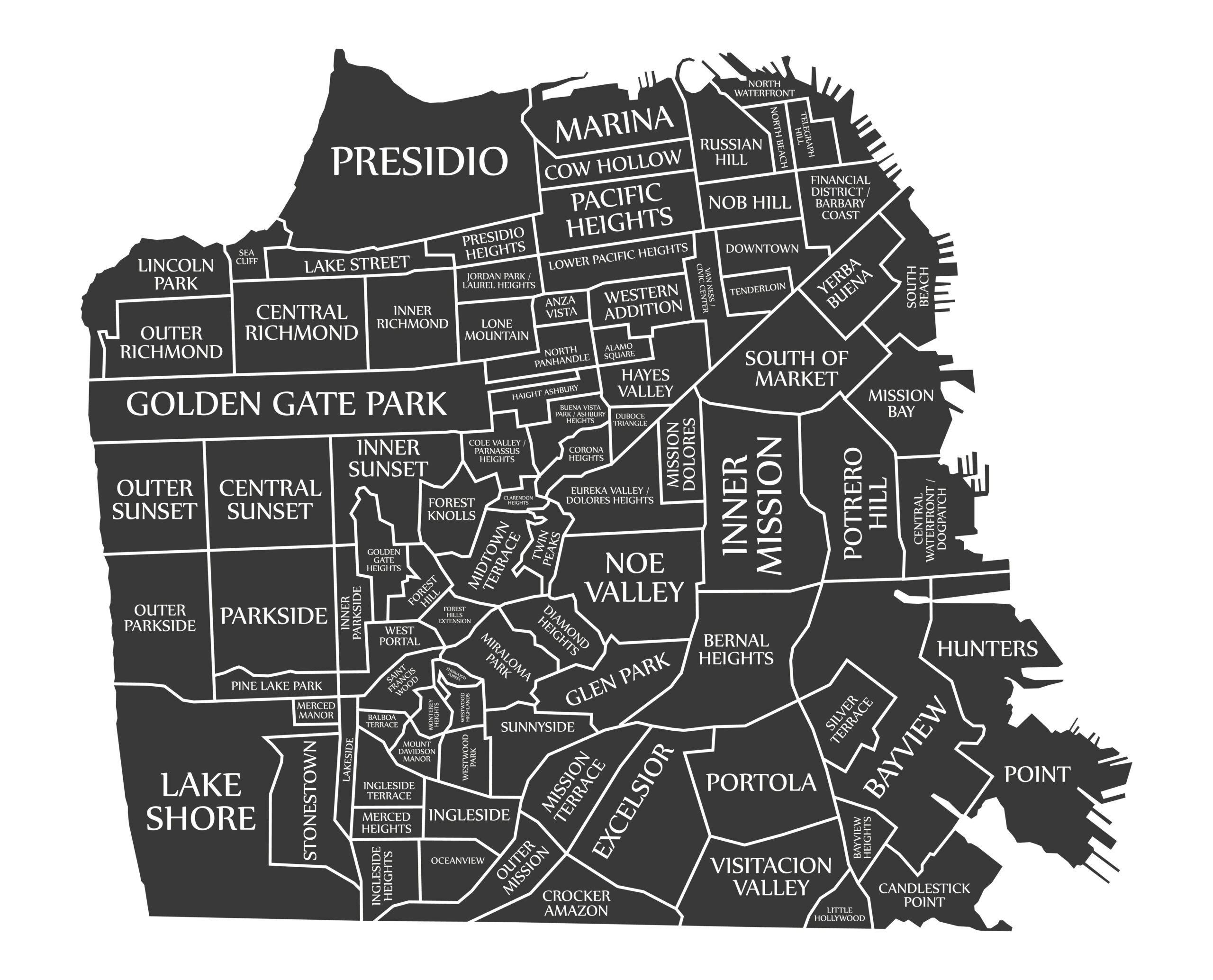
Supervisor Myrna Melgar has introduced legislation that aims to incentivize much-needed family-sized housing on the west side of the city. While clearly in line with the City’s housing production goals, […]

Housing developers in San Francisco no doubt recognize this entitlement moment of disbelief: after a grueling, years-long process of working with staff, neighbors, and policy-makers, with numerous concessions made to […]